


GI bleeding refers to bleeding anywhere in the digestive tract — from the food pipe (esophagus) to the anus. It may appear suddenly or be slow and unnoticed for a long time.
It can be classified as:
⚠️ Important: Even if bleeding stops, the cause must be identified and treated to prevent recurrence or serious complications.
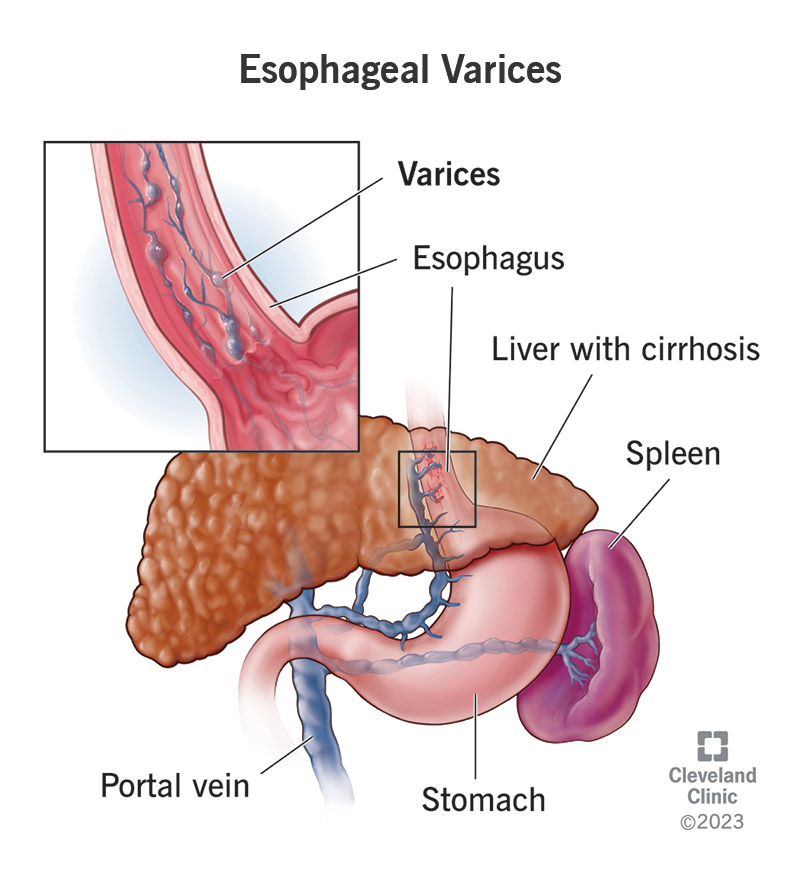
Upper GI Bleeding:
Lower GI Bleeding:
sanghamitragastroenterology@gmail.com
KGH: Pentakota Complex, Maharanipeta
MVP: MIG-55, Sector 5, MVP Colony